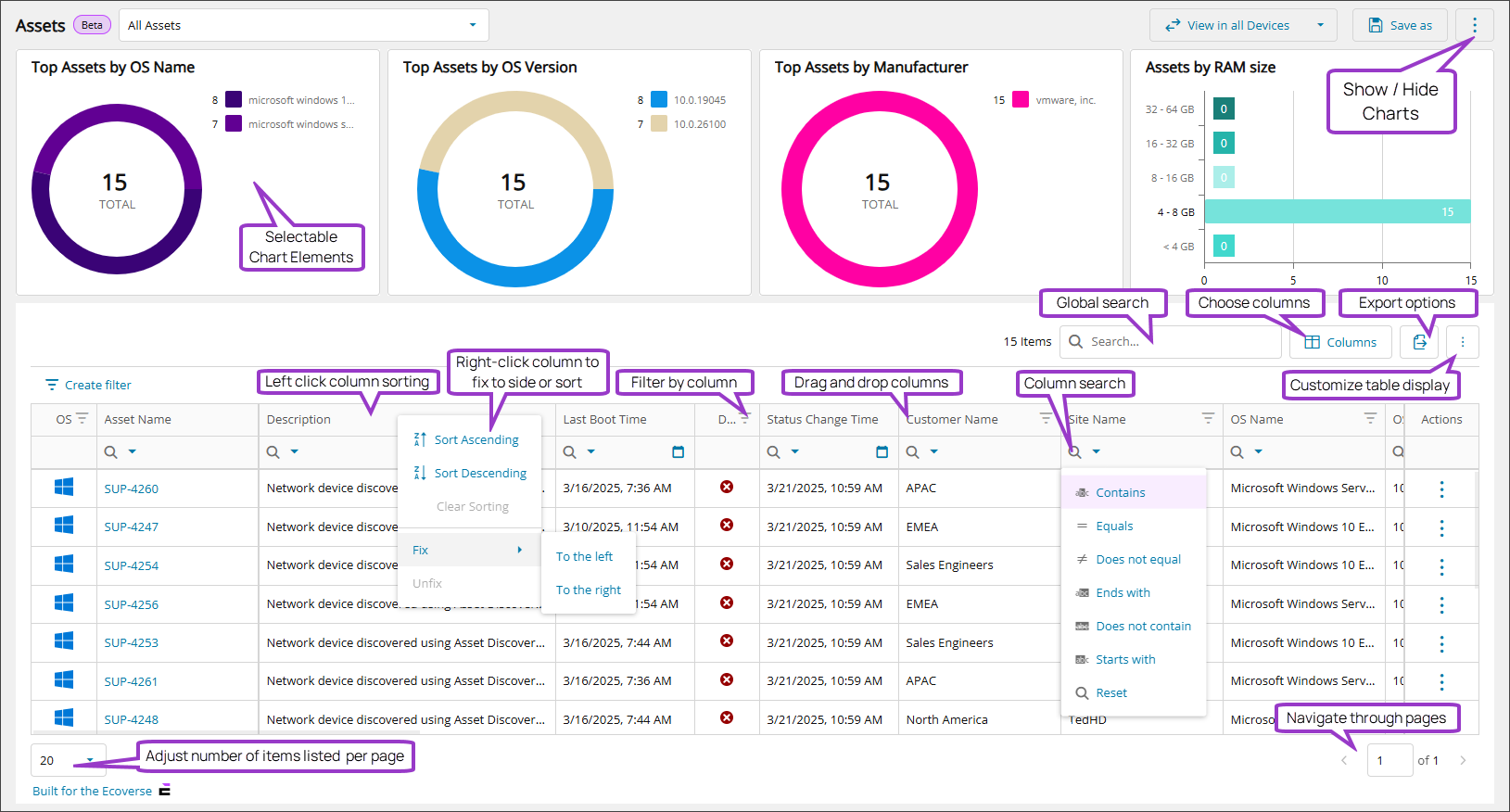
Assets view (New)
Use the Assets view to monitor assets efficiently with filters, searches, and actions. Visualizations, charts, and tables simplify asset tracking and make it easier to find devices and assets. The view helps you spot patterns, trends, and anomalies, revealing opportunities, risks, and areas for improvement. While it's primarily built for help desk technicians, anyone who needs to manage or find assets can use it.
Access the Assets view
- Select Dashboards > Assets in the Left navigation.
Available actions
In the Assets view, you can:
- View asset details
- Show an asset in the All Devices view
- Reboot an asset
- Start a remote access session
- Manage tags
All actions initiated in the Assets view are recorded in the User Audit Report, available from Reports > User Audit Report.
Available columns
In the Assets view, you can select the columns you want to display:
- Asset Name
- A unique identifier for the asset. You can update this in N-central or N-sight.
- Azure ID
- Identifies and tracks individual resources or objects in Microsoft Azure, such as virtual machines, storage accounts, or applications.
- Azure Region
- The geographic location of Azure data centers. Regions help reduce latency and support compliance. Examples: East US, West Europe, Southeast Asia.
- Azure Size
- Specifies the configuration of Azure resources, including CPU, memory, storage, and network performance. It determines the resource capacity and cost of a virtual machine or service. Examples: Standard_B2ms (2 CPUs, 8 GB RAM), Standard_E64 (64 CPUs, 432 GB RAM).
- Azure Subscription
- A billing and access container for Azure services. Each subscription has a unique ID and can be used to separate workloads or environments.
- BitLocker Status
- Shows the current state of disk encryption and protection.
All drives are encrypted.
At least 1 drive is not encrypted.
No drives are encrypted.
- Chassis Type
- The physical enclosure of a device. Examples: Rack-Mount, Blade Chassis, Tower. Provided by the operating system.
- CPU Cores
- The number of processing units within a CPU. More cores improve multitasking. For example, a quad-core CPU can handle four tasks at once.
- CPU Count
- The number of physical processors in a device. For example, a server might have two CPUs, each with multiple cores.
- CPU Name
- The brand and model of the processor. Examples: Intel Core i7-12700K, AMD Ryzen 9 7950X.
- CPU Speed
- Measured in GHz, it shows how many billion cycles the processor performs per second. Example: 3.5 GHz = 3.5 billion cycles per second.
- CPU Type
- The processor’s architecture or category. Examples: x86 (32-bit), x86-64 (64-bit).
- Customer Name
- The name of the client that owns the asset.
- Description
- Notes or comments associated with the device in N-central or N-sight.
- Device Status
- Indicates whether the agent is currently connected to cloud servers.
- External IP
- The device’s external IP address.
- Host Name
- A human-readable name that identifies the device on a network.
- IP Address
- A comma-separated list of IP addresses assigned to the device.
- Last Boot Time
- The last time the device was restarted.
- Logged in Users
- Lists active user sessions for monitoring, security, and compliance.
- MAC Address
- A comma-separated list of MAC addresses. Used to identify and manage devices on a network.
- Manufacturer
- The name of the asset’s manufacturer.
- Memory Total Size (GB)
- The total installed RAM on the device, measured in gigabytes.
- Model
- The model name or number of the device.
- NetBIOS Name
- A short name (up to 15 characters) used to identify a device on a local network. Examples:
OFFICE-PC,MAIN-PRINTER. - OS
- Displays the operating system type:
 Windows,
Windows,  macOS, or
macOS, or  Linux.
Linux. - OS Build
- Displays the operating system’s build version. It reflects the cumulative patch level and update status. (Currently Windows only)
- OS Feature Release
- Displays the operating system's release identifier. For example, 24H2, 25H2.(Currently Windows only)
- OS Install Date
- The date and time the operating system was installed on the device.
- OS Name
- The name of the operating system.
- OS Version
- Details about the OS version, including bit version and build number.
- Patch Management
- The patch engine status appears as an icon. Hover over the patch icon to view the date of the last patch scan.
- Secure Boot
- Shows the secure boot status:
Enabled,
Disabled, or
Status unknown.
- Serial Number
- The device’s serial number.
- Service Organization Name
- The name of the MSP or service organization that manages the asset.
- Site Name
- The name of the client site where the device is located.
- Status Change Time
- The timestamp of the last status change (e.g., from Active to Inactive).
- Tags
- Displays the number of tags assigned to the asset. Hover over the count to view all tags.
- Timezone
- The time zone setting for the asset, used for tracking and optimization across regions.
- TPM Activation
- Indicates whether the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is enabled. TPM adds security by storing sensitive data like encryption keys.
- TPM Version
- The specification version supported by the TPM.
Ecoverse functions
All our new Ecoverse views have common functionality, such as filtering and sorting the presented data, performing searches, and exporting. For full details and instructions, please select a link below.
- Ecoverse views
- Filter and sort Ecoverse views
- Search Ecoverse views
- Create custom filters in Ecoverse views
- Custom filters examples
- Customize your Ecoverse views
- Save Ecoverse views
- Export data from Ecoverse views
As Ecoverse views are developed and released, they may not initially contain full Ecoverse functionality.
Related articles
- Review System and user requirements for Assets view
- Discover Vulnerability Management (New)
- Learn about Ecoverse views
- Read about the new Modern Agent