Approval Policy
Patch Management prevents the Windows Update's optional Updates from being turned ON or OFF by the Device's End Users.
To turn Windows Update's optional Updates back on in the event a device requires Windows Update's optional Update, Patch Management must first be disabled.
Missing patches represent a significant security threat to servers and workstations. Especially as after an update to fix a vulnerability becomes public knowledge, attackers will specifically target the exploit on unpatched devices. In line with security best practices to mitigate the impact of these types of attack it is always advisable to ensure computers are running the latest patches.
Patch Management for Windows requires approval before deploying patches and you can choose the default behavior for how patches are handled.
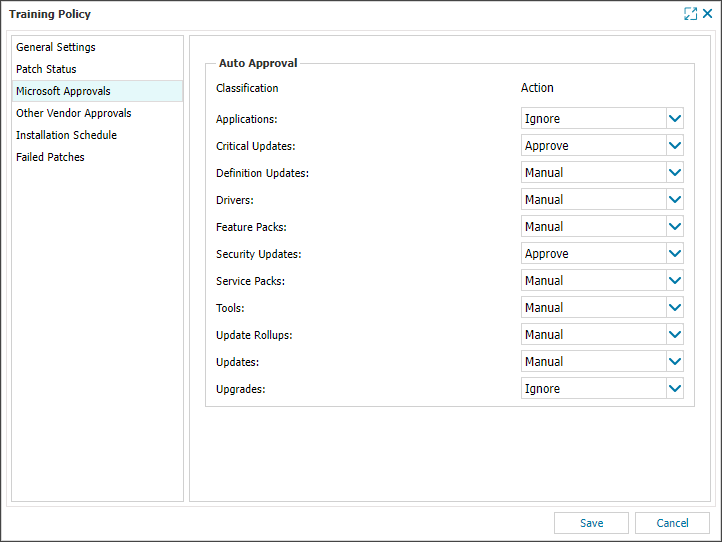
Microsoft software
Patch Management for Windows takes administrative control of Windows Update, ensuring Windows Updates will not attempt to install updates on its own.
See Supported Microsoft applications for the list supported items.
Microsoft updates are based on their classification, see Microsoft patch classifications for more details.
| Default Policy Settings (Server, Desktop and Laptop) | |
|---|---|
| Approve | Critical Updates Security Updates |
| Manual | Definition Updates Drivers Feature Packs Service Packs Tools Update Rollups Updates |
| Ignore | Applications Upgrades |
Please see Microsoft patch classifications for further details on how Microsoft define their classifications.
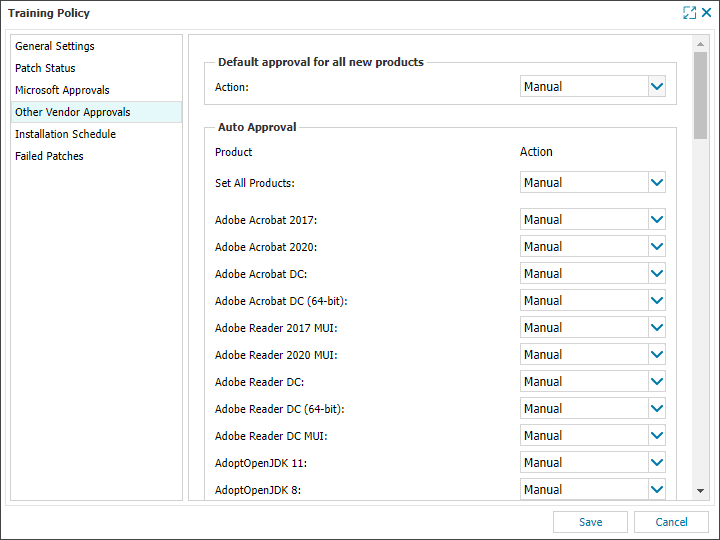
Third-party software
Other software vendors (such as Adobe) the behavior is by product. See Third-party (non-Microsoft) applications for a list of supported software.
| Default Policy Settings (Server, Desktop and Laptop) | |
|---|---|
| Manual | All supported 3rd party software |
Approval behavior
Where patches are set to automatically Approve, they are automatically deployed based on the Installation Schedule and do not require any manual intervention.
You can decide how patches are handled in line with your processes. For example, company policy may dictate that critical patches are rolled-out as soon as possible, whereas all others are trialled in a sandbox environment before deployment.
When patches are set for automatically approval they do not show as missing in the Patch Status Check (as an action is automatically applied for the patch). These patches automatically go to Pending state in the Patches tab and are deployed at the next remediation cycle.
Visit Patch Approval Actions for information on the patch approval hierarchy.