Migrate to standalone DNS Filtering
This article explains the DNS Filtering (DNSF) migration process. The process transitions MSPs from an integrated account (managed through N-central) to a standalone account (managed directly through the DNSF portal). It also describes the differences between the two account experiences and highlights the actions required before, during, and after migration.
Migration steps
After you agree to proceed with migration, N-able completes these steps:
- Rename sites
N-able runs an API on the designated server to rename all the DNSF sites that match N-central service organizations (SOs), customers, and sites. This ensures clarity after migration.
- Disconnect integration
The migration process removes the connection between the N-central server and your DNSF account. N-able submits the migration request to DNSF partners, who complete the transition to a standalone account.
- Disable DNSF rules
N-able disables DNSF-related rules on the N-central server.
- Start migration
N-able runs the DNSF API to start the migration process on the N-central server and all associated devices.
The migration process may take up to 30 days. During this time, you may still see DNSF integration indicators in N-central.
Compare experiences before and after migration
DNSF integration menus
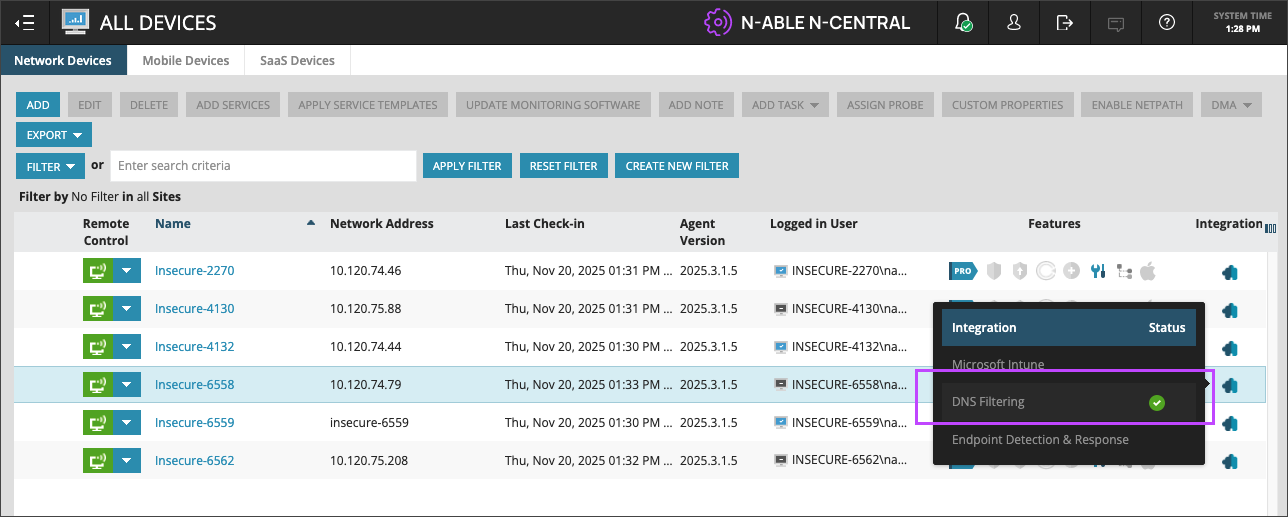
DNSF integration indicators
- Before migration: Visible in the All Devices view.
- After migration: Visible in the All Devices view, but only for up to 30 days, until complete.
Rule and policy management
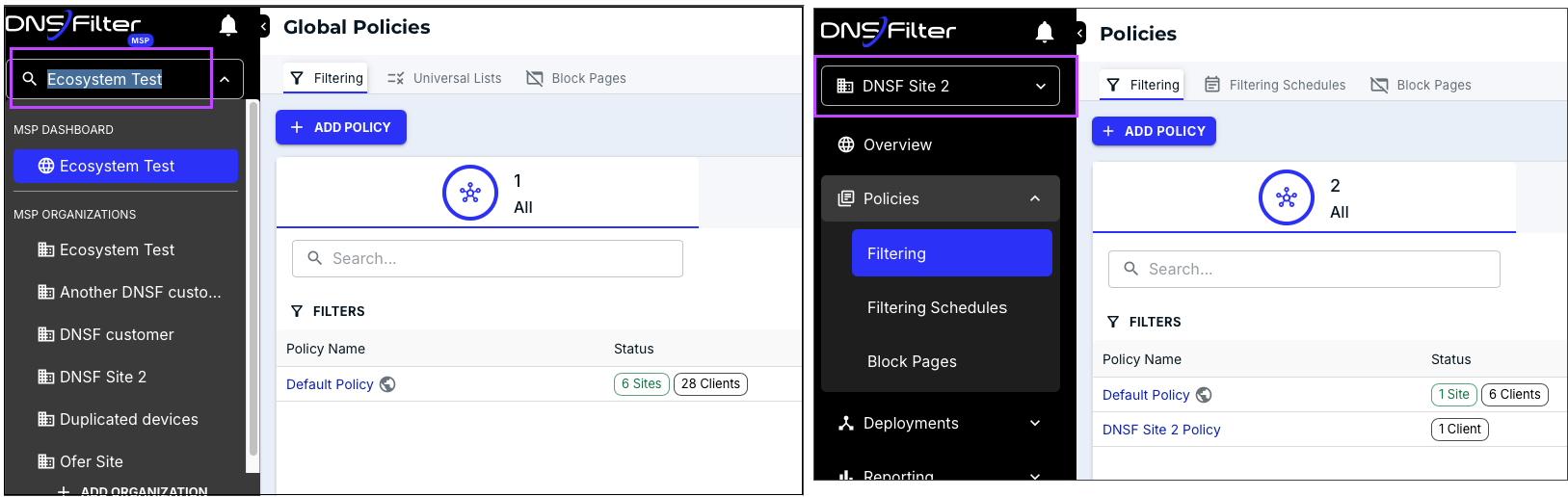
- Before migration: Managed in N-central. Filtering profiles or policies are created as global policies.
- After migration: Managed in the DNSF portal.
- Policies assigned in N-central migrate to the DNSF portal.
- Unaassigned policies in N-central migrate and remain available for you to assign.
- You can create and manage policies for each MSP organization. For example, a policy created for DNSF Site 2 applies only to devices under that site. It isn’t available at the System level, which is the Ecosystem Test MSP account.
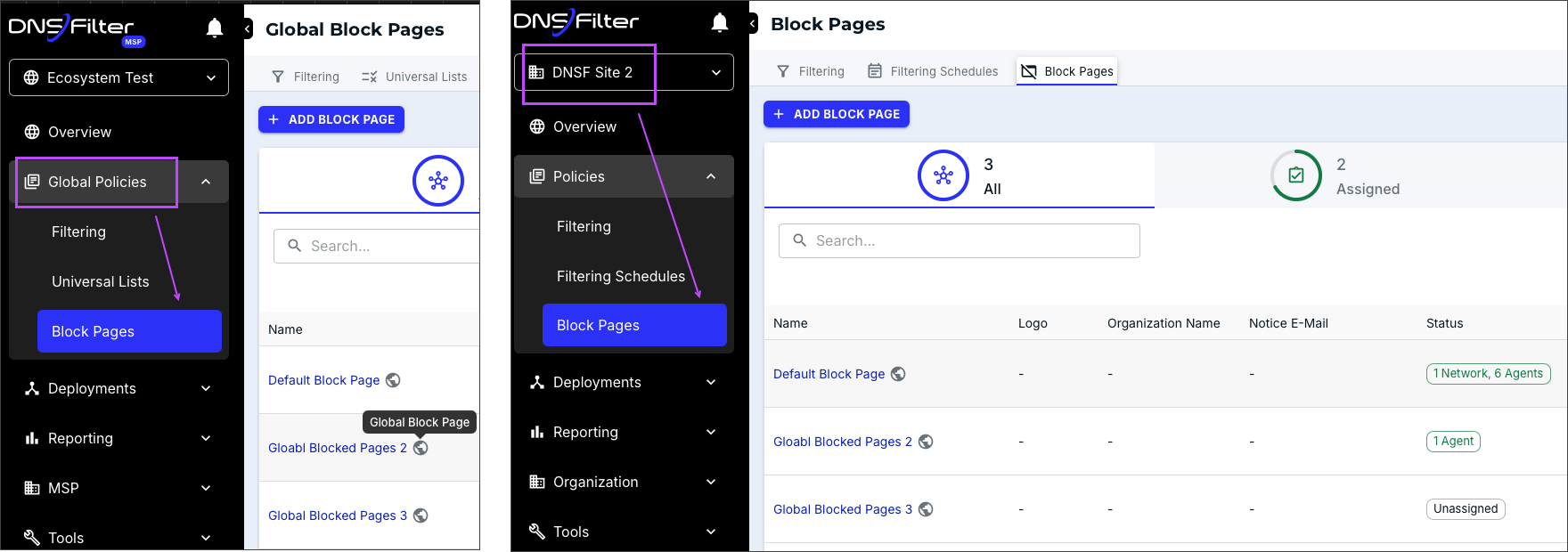
- You can create global policies at the MSP account level and apply them to any MSP organization. For example, you can define global blocked pages at the MSP account level and apply them to any site.
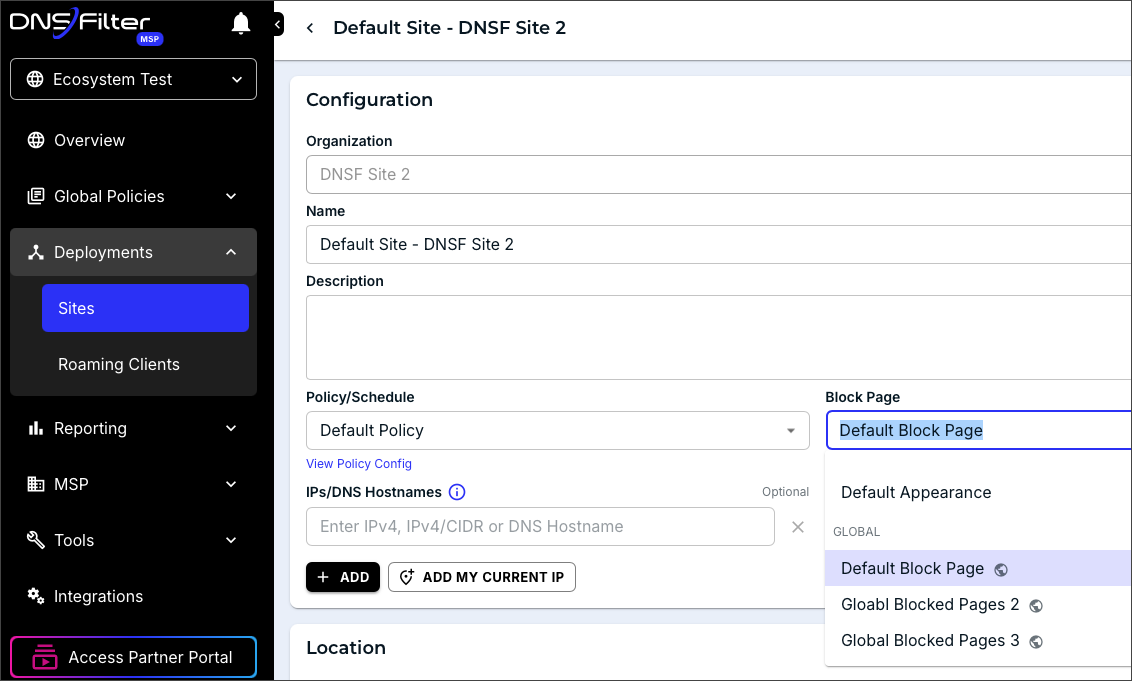
- You can set default policies and block pages for MSP organizations.
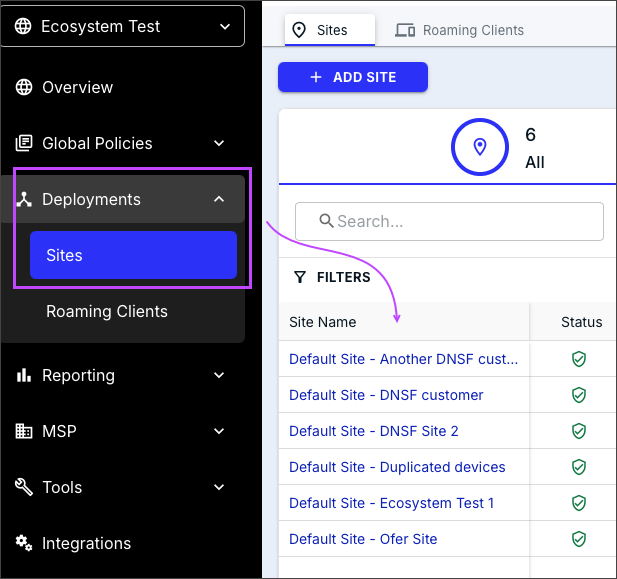
- You can manage devices across sites.
DNSF agent control
- Before migration: DNSF agent installed or removed using N-central.
- After migration: Managed using the DNSF portal or directly on devices.
Ecosystem agent behavior
- Before migration: Uninstalling the Ecosystem agent removes the DNSF agent.
- After migration:
- The Ecosystem agent should not be present on devices unless other integrations, such as Intune or EDR, are active.
- If the Ecosystem agent is still present on devices and you manually uninstall it, the DNSF agent should remain installed—unless a communication issue with the N-central server prevented the devices from being marked as migrated.
Changes to DNSF portal access
| Role | DNSF portal before migration | DNSF portal after migration |
|---|---|---|
| MSP | No access | Full access to your DNSF portal |
| N-able | Full access | No access to your DNSF portal |
Review how the DNSF portal structure changes
The DNSF portal structure differs between integrated and standalone accounts.
Integrated account structure
Device visibility is based on the user’s level in N-central. For example, users at the site level see only that site’s devices. Users at the SO level can access all devices under that SO and drill down into customers and sites.
CustomerServer ├── SO1 │ ├── Customer1 │ │ ├── Site1 │ │ └── Site2 │ └── Customer2 ├── SO2 │ └── Customer1 │ ├── Site1 │ └── Site2
Standalone account structure
In the standalone DNSF portal, you see all customers at the same level with no hierarchy of SOs, customers, or sites. All site names are distinctive and related to each through the Rename API.
SO1 SO1_Customer1 SO1_Customer1_Site1 SO1_Customer1_Site2 SO2 SO1_Customer2 SO2_Customer1_Site1 SO2_Customer1_Site2
You can also see all customer devices in a single list and filter to show data for a specific MSP organization. Use the MSP organization dropdown list to select the organization you want to manage. From there, you can manage devices and apply policies.
Take action after migration
After the migration is complete, you may need to take the following actions in the DNSF portal:
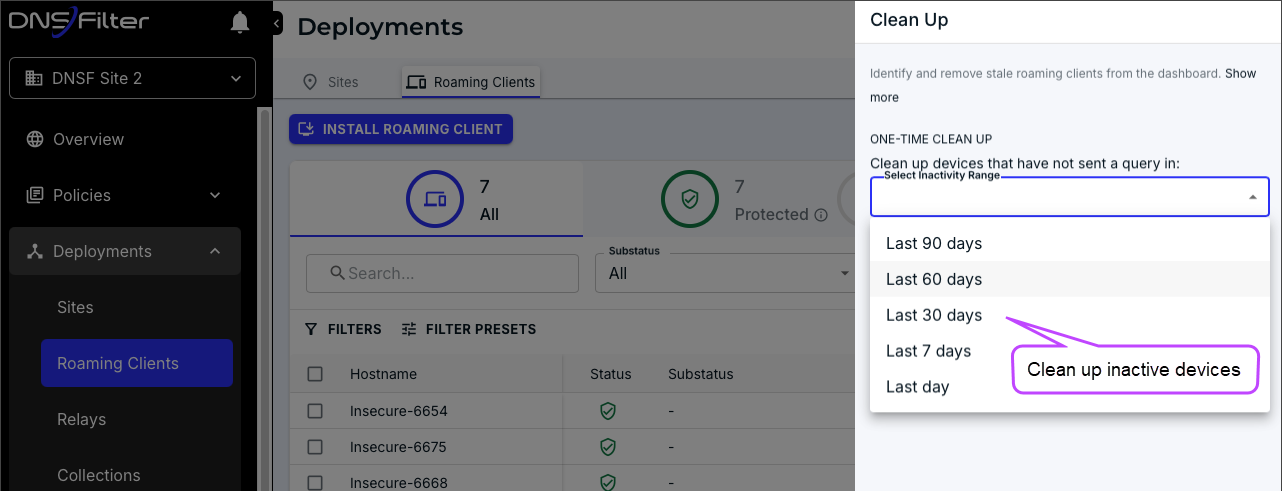
- Clean up inactive devices: Remove DNSF devices that haven’t been active for more than 30 days.
- Review reappearing devices: Devices previously deactivated or deleted may reappear due to the migration process.
- Manage policies and rules: Review and adjust migrated DNSF policies and rules as needed.
- Organizational cleanup: Remove empty organizations or sites that were created during migration but do not contain devices.