Patch Management
N-able N-central provides an automated Vulnerability and Patch Management solution designed to reduce the attack surface across managed endpoints. It ensures that devices remain protected by systematically identifying vulnerabilities and applying updates based on intelligent policies and insights.
Assess and Prioritize Patches
Detected vulnerabilities are evaluated using industry-standard metrics like CVSS scores, allowing IT teams to prioritize remediation based on risk.
-
Visibility into missing patches by severity level
-
Group and device-level reporting dashboards
-
Tagging of critical, moderate, or low-risk vulnerabilities
Deploy Patches Automatically
N-central enables centralized, policy-based automated patching for Windows and third-party software. Administrators can configure schedules, reboot options, maintenance windows, and fallback behaviors.
-
Fully automated or approval-based patch workflows
-
Patch caching and bandwidth control using probe-based deployment
-
Post-patch reboot and rollback options
Manage Offline Patches
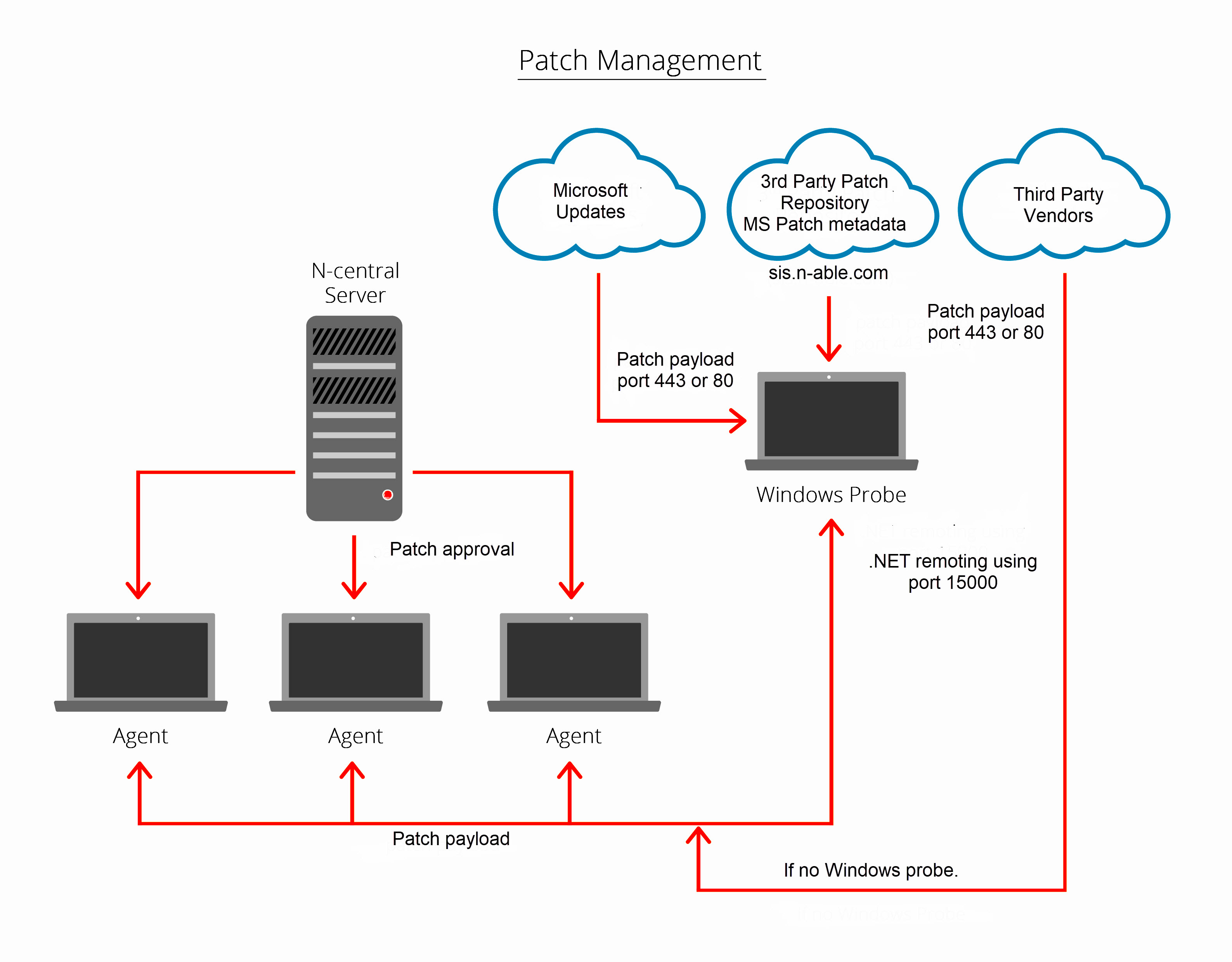
N-central archives metadata for a subset of system patches including Cumulative Updates, Security Only patches, SSUs, and third-party patches on, on sis.n-able.com. Probes retrieve this metadata to deliver updates to devices in offline patching mode, which operates similarly to online patching.
Communication with sis.n-able.com uses port 443.
Offline patching uses MSU installer files instead of the CAB installer files that are used with online patching, using the Microsoft Update server. The base URL of these files might also differ from those with online patching.
Patching data for offline devices is done through the probe using port 15000.
Monitor for missing patches
Installing a Windows Agent on a device automatically adds the Patch Status v2 service. This service queries the local Windows Update Agent (WUA) to identify missing Microsoft and third-party application patches. The Patch Status service shows
Total missing patches
Displays the total number of Microsoft and supported third-party patches that the device requires but has not yet installed.
-
Excludes superseded patches to avoid false positives.
Patches installed with errors
Flags patches that attempted to install but failed.
-
Requires administrators to investigate and remediate through patch troubleshooting workflows.
Missing patches by category
Groups missing patches by type, such as security updates, critical updates, or feature updates.
-
Allows prioritization of high-impact security patches.
Missing patches older than a user-specified number of days
Highlights patches that remain uninstalled beyond an administrator-defined age threshold.
-
Highlights devices that may be out of compliance.
Patches missing but not yet approved
Shows patches identified by WUA as missing but still pending approval in N-central (manual or automatic).
-
Keeps these patches in the missing list until approval occurs. These unapproved patches represent a critical blind spot in many organizations' security posture, as they may include high-risk vulnerabilities that are not yet scheduled for remediation.
Compliance and Reporting
To support compliance frameworks (for example, HIPAA, ISO 27001), N-central includes built-in reports and audit trails showing patch status and remediation timelines.
-
Audit-ready patch compliance reporting
-
Proof of remediation for regulatory requirements
-
Executive summaries and technician-level detail
Security Integration
Patch deployment workflows are hardened by the N-central secure agent communication. All patch metadata and deployment instructions are transmitted over TLS-encrypted channels, with role-based access control (RBAC) ensuring that only authorized users can modify policies or force patch actions.
Manage Windows Updates
Windows patch management in N-able N-central uses a coordinated process between the Windows Patch Management Engine (PME) Agent, the local Windows Update Agent (WUA), and N-central components such as Probes and Agents. This process ensures that devices receive the correct updates based on administrator-defined approvals and deployment schedules.
Windows update process flow
The PME Agent queries the WUA to retrieve a list of available updates, sends this information to the N-central server, and then works through a controlled approval and deployment workflow. Once updates are approved, the PME coordinates with Probes or other Agents to download and distribute the updates efficiently, maintaining control over bandwidth usage and installation timing. This method ensures consistent and reliable patch deployment across managed devices:
-
The Windows Patch Management Engine (PME) Agent communicates with the local Windows Updates Agent (WUA) and requests a list of available updates.
-
The Windows Agent sends this information to the N-able N-central server.
A device can send data directly through another path. See Direct data submission for details.
-
The N-able N-central administrator configures approvals for the list of updates.
-
The Windows Agent (PME) communicates with the Probe and/or Agent and requests the approved updates.
-
The Windows Agent downloads the required patch files directly from _sis.n-able.com_/the Microsoft update cloud.
Alternatively, when Probe patch caching is enabled, the Windows Agent requests the required patch files from the probe. The probe then downloads the files directly from sis.n-able.com or the Microsoft update cloud.
-
The Windows Agent applies the schedule for installing updates.
Direct patch data submission
The Windows Agent sends monitoring and asset data to the N-able N-central server. However, this is not the only data submission path. Some devices can send patch data directly to our N-able cloud-based patch metadata service.
Devices selected for direct patch submissions must
-
Have access to the internet.
-
Connect to SIS (sis.n-able.com), the N-able Software Information Service.
-
Reach AWS endpoints (*.amazonaws.com) to communicate with cloud-hosted services.
Direct patch data submission allows devices to retrieve patch metadata efficiently and optimize patch management processes through cloud connectivity.